News
Sep 27, 2021. We are starting a new collaboration project with pSemi to develop a 28 GHz V2X testbed.
July 1, 2021. We have open-sourced the MVDNet dataset and model implementation (https://github.com/qiank10/MVDNet). MVDNet dataset represents the first radar-lidar dataset with accurate vehicle labels.
June 1, 2021. We are setting up a collaboration project with Keysight and Safe Dynamics, and using our 3D ray tracing framework to reassure the RF safety of 5G mmWave networks.
Aug. 31, 2020. A first version of our 3D ray tracing code and data has been released.
Aug 20, 2020. Our source code for large-scale 3D ray-tracing will be released soon.
Jul 20, 2020. Our paper Demystifying Millimeter-Wave V2X: Towards Robust and Efficient Directional Connectivity Under High Mobility is accepted by Mobicom’20
Feb 20, 2020. Our paper X-Array: Approximating Omnidirectional Millimeter-Wave Coverage Using an Array of Phased Arrays is accepted by Mobicom’20.
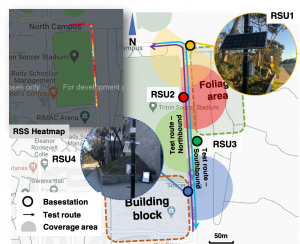
Overview
We present the first comprehensive reality check of mmWave V2X networks. We deploy an experimental testbed to mimic a typical mmWave V2X scenario, and customize a COTS mmWave radio to enable microscopic investigation of the channel and the link. We further construct a high-fidelity 3D ray-tracer to reproduce the mmWave characteristics at scale. With this toolset, we demystify the practicality of mmWave V2X networking under high mobility, and evaluate the potential multiplexing gains that can be achieved in mmWave V2X through Tx/Rx beamforming, multi-array co-phasing, or hybrid beamforming.
Please check our paper for more details.
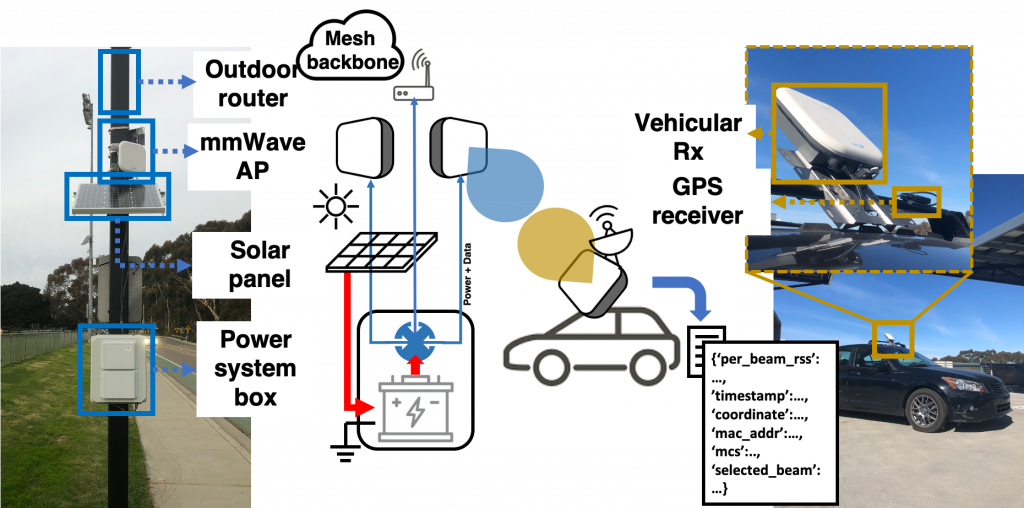
Testbed
We deploy a mmWave V2X network testbed and customize the radios to enable codebook redesign, beam switching, multi-array operations, and real-time channel quality measurement. The deployment follows the 3GPP guidelines, and can be easily reproduced due to its low cost.
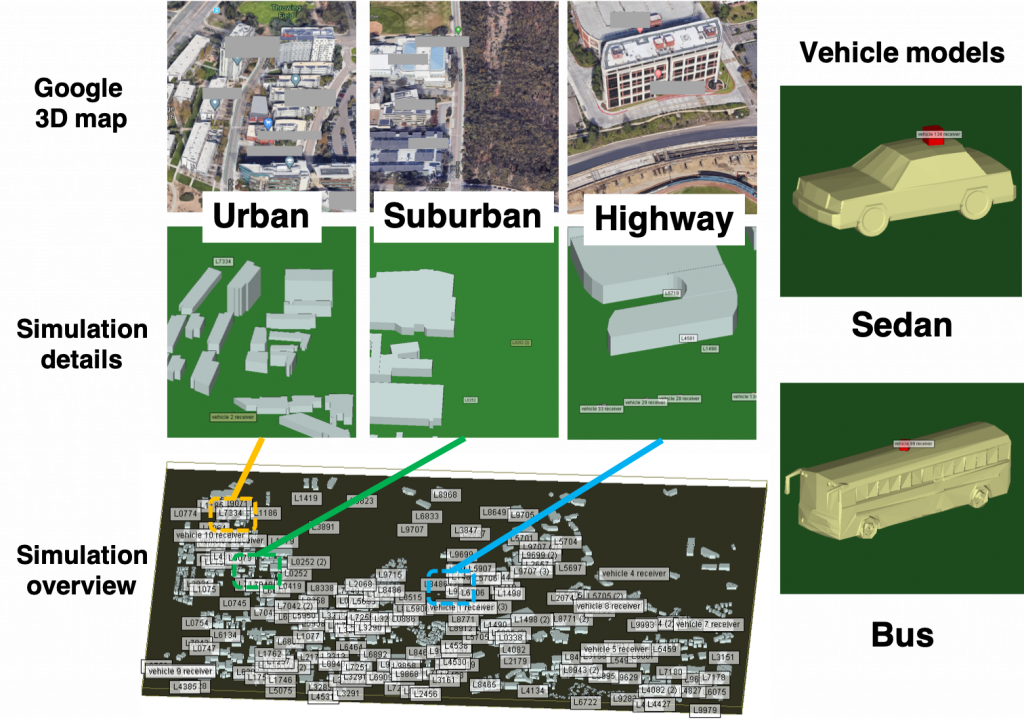
Large-scale 3D ray-tracing
To represent a realistic V2X environment, our ray-tracing simulator takes the real-world 3D map as input, and places various moving vehicles on the roads based on the SUMO vehicular traffic generator. We then use Wireless Insite, a commercial ray-tracing simulator, to track the propagation effects of the mmWave signals (including reflection, scattering, and penetration) and derive the channel/link characteristics.
Please check our paper for more details. See below to find our 3D ray-tracing source code and datasets.
Multi-panel mmWave radio
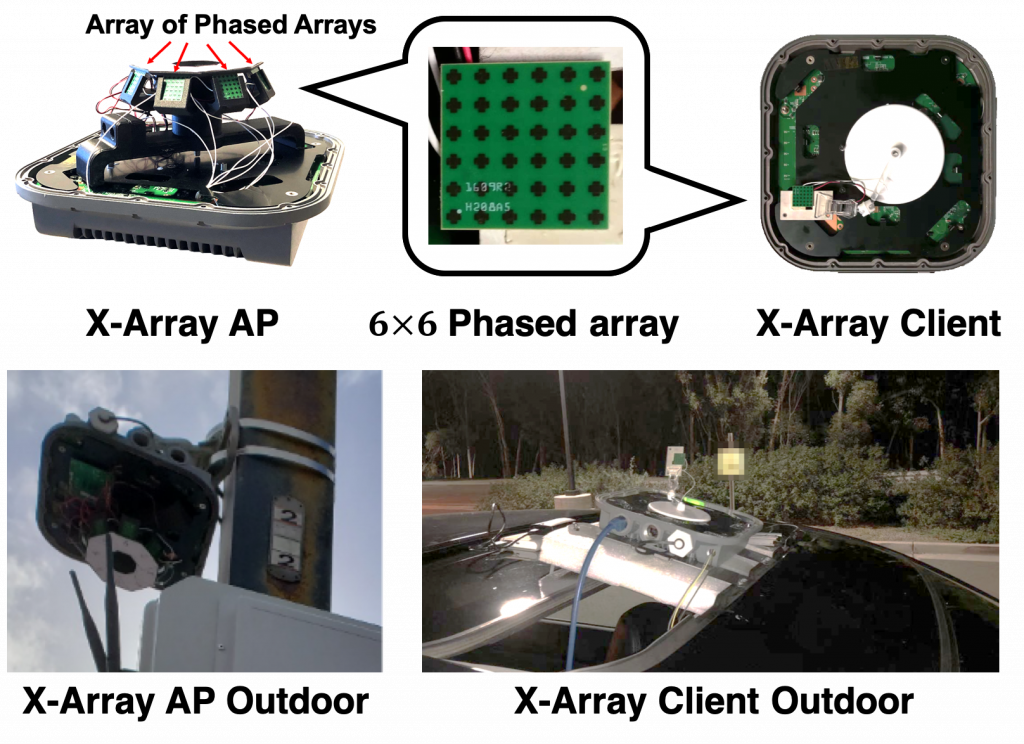
To fully exploit the potential of the multi-panel mmWave radio, we propose a novel multi-panel mmWave system: X-Array, which jointly selects the arrays and beams, and applies a dynamic co-phasing mechanism to ensure different arrays’ signals enhance each other. Our X-Array solution framework builds on the 802.11ad standard and runs directly on commodity devices. Our experiments have verified X-Array’s advantages in terms of efficiency, coverage, and ability to rapidly recover from link outage.
Please check our paper for more details.
Source Code and Datasets
Note: a valid Wireless Insite license is required to run our 3D ray-tracing code.
- Datasets
- 3D ray-tracing source code (including the scripts to move objects in WI simulations and create batch simulations from SUMO traffic pattern)
Citing our papers
Demystifying Millimeter V2X:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3372224.3419208,
author = {Wang, Song and Huang, Jingqi and Zhang, Xinyu},
title = {{Demystifying Millimeter-Wave V2X: Towards Robust and Efficient Directional Connectivity Under High Mobility}},
year = {2020},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3372224.3419208},
doi = {10.1145/3372224.3419208},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 26th ACM Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (MobiCom)},
}Multi-panel mmWave radio:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3372224.3380882,
author = {Wang, Song and Huang, Jingqi and Zhang, Xinyu and Kim, Hyoil and Dey, Sujit},
title = {{X-Array: Approximating Omnidirectional Millimeter-Wave Coverage Using an Array of Phased Arrays}},
year = {2020},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3372224.3380882},
doi = {10.1145/3372224.3380882},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 26th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking}
}Contact
If you have any questions on our 3D ray-tracing or testbed, please contact us.
- Song Wang, PhD student @ UC San Diego, email: sowang@ucsd.edu
- Jingqi Huang, MS student @ UCSD (Now PhD student @ Purdue University), email: huan1504@purdue.edu
- Xinyu Zhang, Associate Professor @ UC San Diego, email: xyzhang@ucsd.edu
Acknowledgement
M3 is currently supported by the NSF CCRI program (grant number CNS-1925767). We also acknowledge the gracious equipment donations/loans from Samsung Research America and National Instruments.